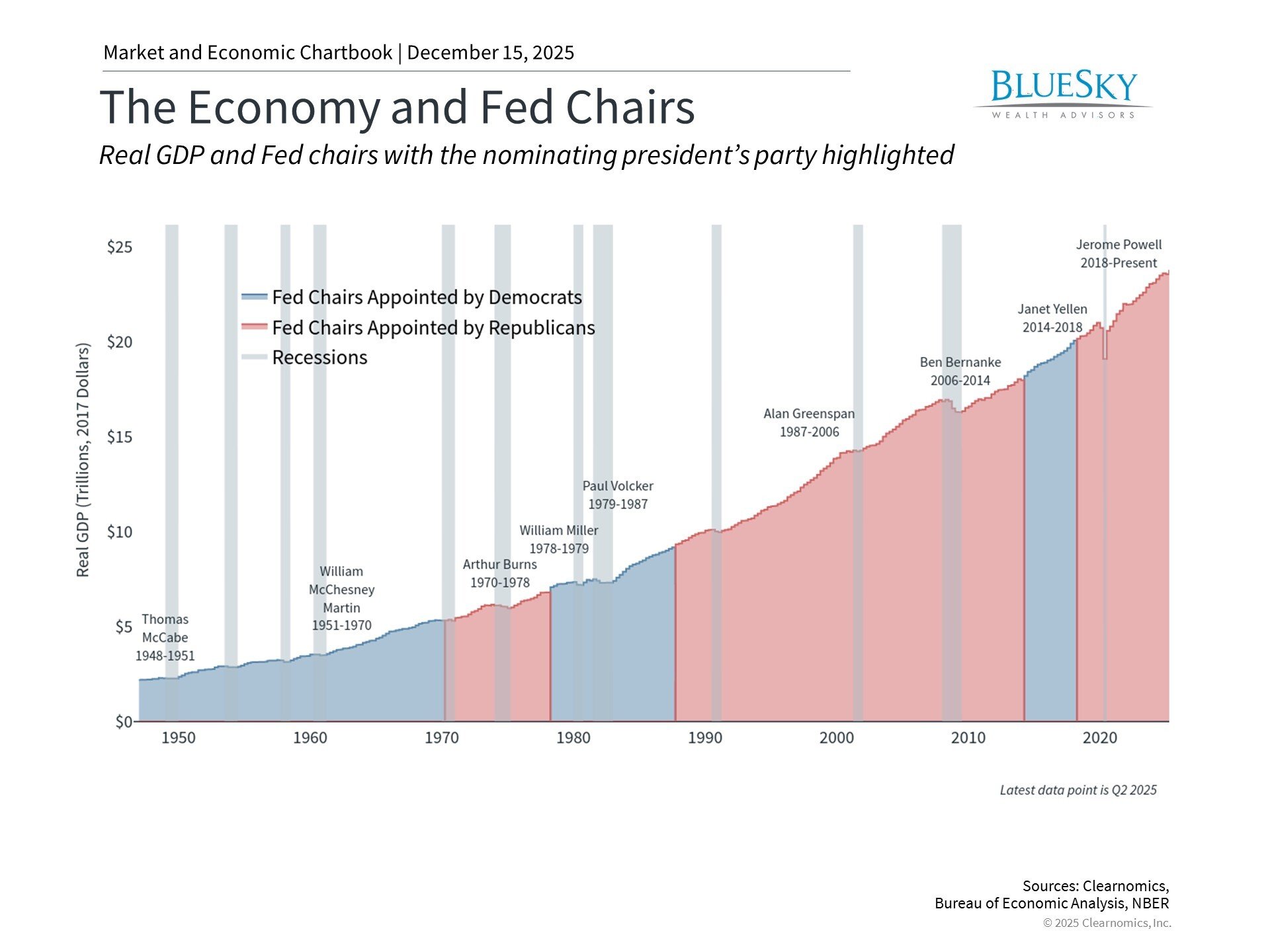
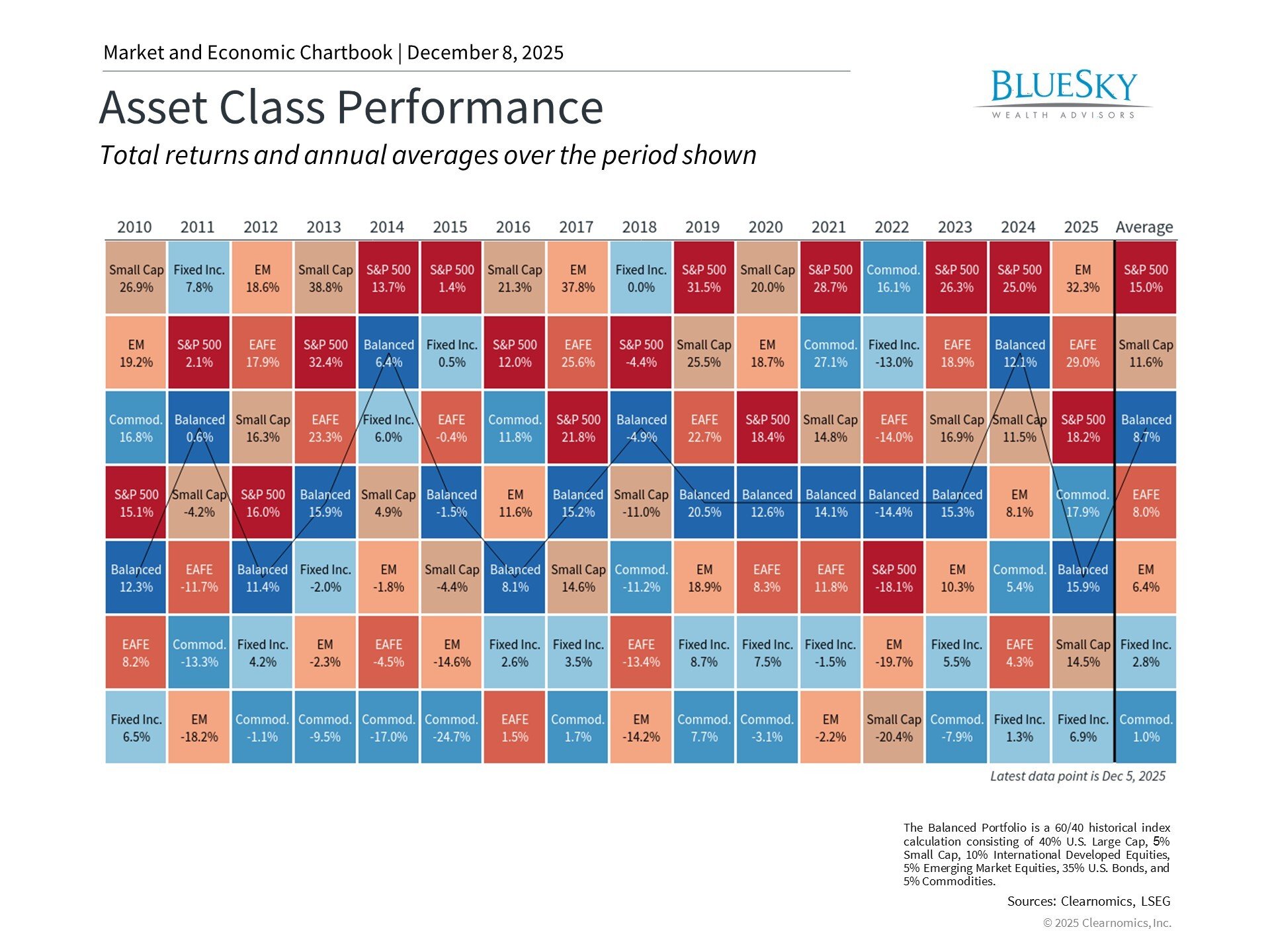
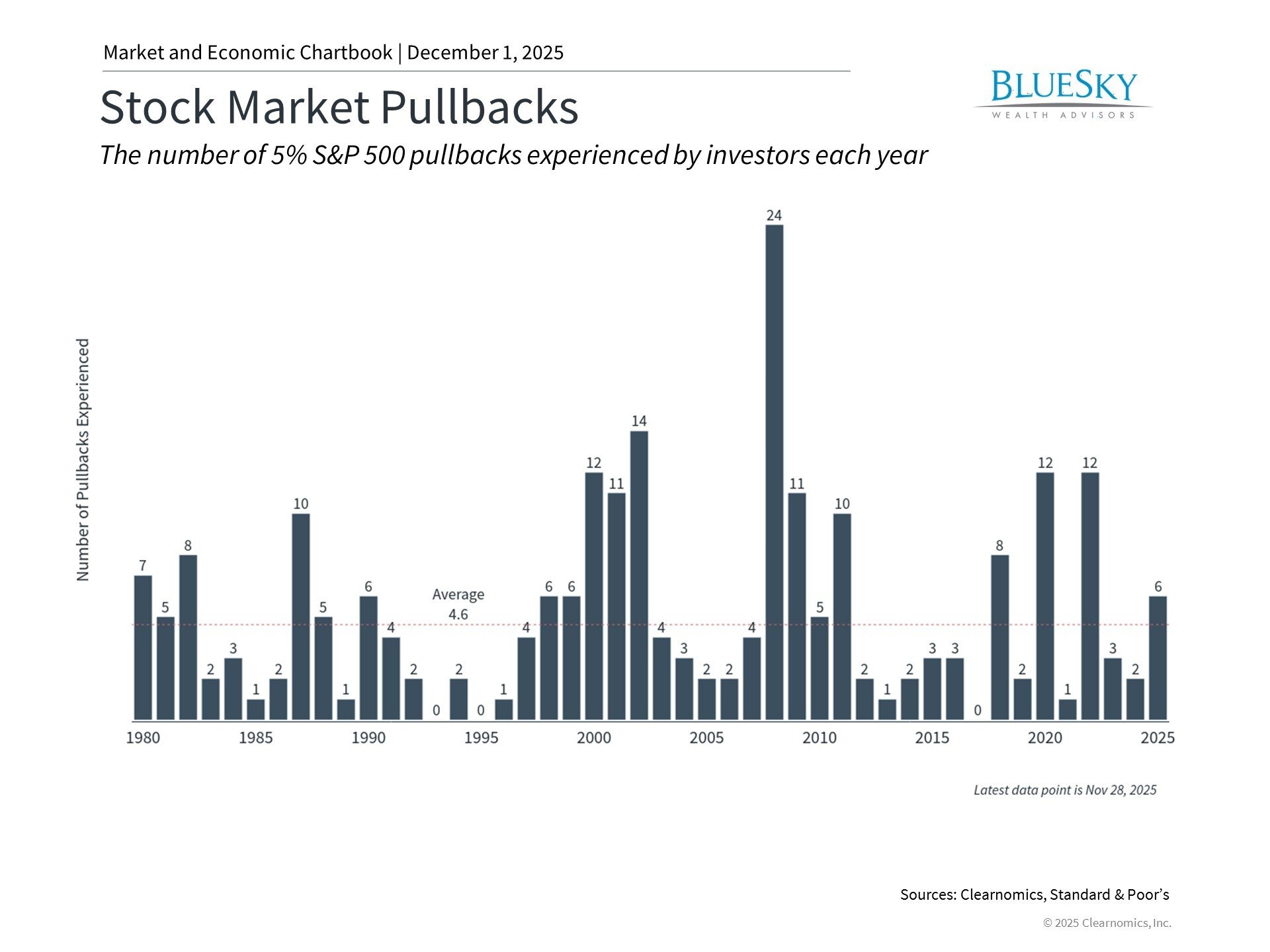
What Investments Are Inflation Proof?
What Investments Are Inflation Proof?

In the turbulent seas of economic uncertainty, inflation looms large, threatening to erode the value of your hard-earned wealth. It’s a relentless force, insidiously chipping away at the purchasing power of your investments over time. However, not all is lost in this battle against inflation. There exist investment vehicles and robust lifeboats that can weather the storm, preserving and even growing your wealth in times of rising prices.
These are ‘inflation-proof’ investments, powerful tools that can provide a sturdy bulwark against the ravages of inflation. But what exactly are these inflation-proof investments? How do they work? And most importantly, how can you incorporate them into your financial strategy? Dive deeper into our comprehensive guide on inflation-proof investments to unravel these questions. Keep reading to equip yourself with the knowledge necessary to navigate the fluctuating tides of inflation with confidence and foresight.
What are Inflation-Proof Investments?

Inflation-proof investments, also known as “real return” or “inflation hedged” investments, are financial assets that aim to deliver returns over and above the inflation rate, thereby maintaining the purchasing power of your wealth over time. Unlike conventional investment avenues, such as bonds or cash, whose real value can be severely hit by inflation, these investments have intrinsic qualities that allow them to keep pace with, or even outperform, inflation. They include various assets such as commodities, real estate, inflation-indexed bonds, or certain dividend-paying stocks.
For instance, consider real estate, a classic inflation hedge. As inflation causes the consumer price index level to rise, property values and rents increase correspondingly. So, if you own a rental property, not only could the property’s value keep pace with inflation, but you could also raise rents over time, thereby ensuring a steady, inflation-beating income. Similarly, government bonds, like Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) in the United States, have their principal amount adjusted in line with inflation, ensuring investors’ returns are not eroded. Thus, incorporating such assets into your portfolio can help protect against the potential detrimental effects of inflation on your investments.
Types of Inflation-Proof Investments

Inflation-proof investments can be classified into different types based on underlying assets or characteristics. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common and effective types of inflation-proof investments:
Commodities
Commodities are tangible goods intrinsic to our daily lives and hold significant value in the global economy. They include resources such as gold, oil, natural gas, agricultural products, etc. The principle of supply and demand primarily governs the prices of commodities. During periods of inflation, the costs of goods and services rise; consequently, the price of commodities also tends to increase. This attribute makes commodities a powerful hedge against inflation.
For example, consider gold, a prized asset since ancient times. Gold is considered a ‘store of value’ because its worth does not diminish over time. When inflation leads to a decrease in the purchasing power of money, investors often flock to gold, driving its price up. Owning commodities like gold can shield you against inflation’s eroding effects, preserving your wealth’s value. However, it’s crucial to remember that commodities can be volatile and influenced by many factors, including geopolitical events, weather patterns, technological changes, etc.
Real Estate
Investing in real estate provides a compelling defense against inflation. The value of properties typically rises in line with general price levels, making it an attractive hedge. As inflation takes hold, the costs of labor and construction materials, which are key factors in real estate valuation, tend to increase. This, in turn, boosts the value of completed properties. Moreover, rental rates often rise alongside inflation, offering property owners an expanding income stream that counterbalances the eroding effects of rising prices.
Consider a rental apartment in a thriving urban area as an example. When inflation spikes and the cost of living in the city rises, landlords can increase rents to maintain the real value of their income. Over time, as the property appreciates in value, the owner can choose to sell, potentially realizing a substantial profit adjusted for inflation. Therefore, a carefully selected and well-managed real estate investment can serve as a robust safeguard against inflation, preserving and even enhancing the purchasing power of your wealth.
However, like any investment, real estate carries risks and should ideally be part of a diversified portfolio. Understanding market dynamics and specific locations and maintaining the property in good condition are crucial factors to consider when investing in real estate.
Inflation-Indexed Bonds
Inflation-indexed bonds, also known as linkers or index-linked bonds, are fixed-income securities whose principal and interest payments are linked to the prevailing inflation rate. As inflation rises, the value of these bonds increases accordingly, ensuring that the investor’s returns keep pace with rising prices. For example, suppose you invest $100 in a 10-year inflation-indexed bond with an annual interest rate of 3%. If the current inflation rate is 2%, your investment would be worth $120 at the end of ten years. This attribute makes these bonds attractive for investors seeking protection against inflation risk.
Several governments, including the United States and the United Kingdom, issue inflation-linked bonds as part of their public debt securities offerings. However, like any index-linked bond investment, these bonds carry default risks and fluctuations in interest rates, so they should be carefully evaluated before adding them to your portfolio.
Dividend-Paying Stocks
Companies with a history of paying regular dividends are often viewed as an effective hedge against inflation. These firms, commonly known as ‘dividend aristocrats,’ typically have a strong market presence, stable earnings, and robust financial health, which empower them to distribute regular dividends to shareholders irrespective of the market conditions. During inflationary periods, these dividends can provide a steady source of income that may potentially outpace the rate of inflation, thereby helping to preserve the investor’s purchasing power. It’s like having inflation-indexed securities that remain unaffected by the fluctuating value of money due to inflation.
For example, if your company pays a dividend of $1 per share, and the inflation rate is 3%, in one year, your purchasing power would be $0.97 (adjusted for inflation). However, if the company increases its dividend payout by 5% to keep up with rising prices, your purchasing power will remain unchanged at $1. This aspect makes dividend-paying stocks attractive for investors seeking inflation-proof investments. However, it’s worth mentioning that, like any stock investment, these stocks carry risks and require careful analysis and diversification for optimal returns.
TIPS (Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities)
Another popular inflation-proof investment option is TIPS (Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities), issued by the US Treasury Department. Like traditional bonds, these have a fixed interest rate, but their principal value is adjusted for inflation. As inflation rises, so does the value of the bond’s principal amount, ensuring that investors receive returns that keep up with the rising prices.
The interest payments on TIPS are also inflation-adjusted, providing investors with a stable income source that can outpace inflation. For example, if you invest $10,000 in a TIPS bond with an annual interest rate of 3% and the inflation rate for that year is 2%, your investment would be worth $10,300, and you would receive an interest payment of $300. This feature makes TIPS a favorable investment for investors looking to protect their wealth from the effects of inflation. However, as with any other bond investment, it’s essential to consider factors like liquidity risks and fluctuations in interest rates when investing in TIPS.
Crypto Assets
Crypto assets, a relatively new class of digital assets, have demonstrated some degree of resilience to inflation in recent years. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others function on decentralized platforms, and their value is not directly linked to the performance of any specific national economy or its inflation rate. This independence from traditional financial systems offers a potential hedge against inflation.
Let’s take Bitcoin as an example. Bitcoin has a maximum supply limit of 21 million coins, a feature that inherently guards it against inflation. As it becomes more difficult to mine new Bitcoins, scarcity drives up its value, particularly in inflationary periods when traditional currencies lose purchasing power. In fact, during the pandemic-fueled inflation of 2020, Bitcoin saw a significant increase in value, demonstrating its potential as an inflation-resistant asset.
However, investing in crypto assets is not without risks. These include extreme volatility, regulatory uncertainties, and security concerns related to digital wallets and exchanges. Therefore, like any other investment, thorough research and careful consideration of risks and rewards are essential before incorporating crypto assets into an inflation-proof investment portfolio.
Factors Affecting Inflation-Proof Investments

While several investment options offer some degree of protection against inflation, it’s important to understand the factors that determine which investments are more suitable for this purpose. These include:
Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in safeguarding investments against inflation. These rates are determined by central banks such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the Bank of England in the UK. They exert significant control over inflation levels. Higher interest rates have the effect of curbing economic activity, thus reducing inflationary pressure.
Conversely, lower interest rates encourage spending and can contribute to increased inflation. Understanding the relationship between interest rates and inflation is vital for formulating a sound investment strategy. For instance, fixed-income investments like bonds become more attractive when interest rates are high due to higher returns. However, it is important to consider the impact of inflation on these investments.
If inflation is expected to outpace the interest rates, the real return on these investments could be diminished after accounting for inflation. To illustrate, let’s consider an example: if you have a bond that pays an annual interest of 5%, but inflation is running at 3%, your real return is only 2%. If inflation increased to 6%, your purchasing power would be eroded despite the interest received. Therefore, grasping the connection between interest rates and inflation is crucial for making well-informed investment decisions.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions are intrinsically connected to inflation rates and, thus, are pivotal in choosing inflation-proof investments. In periods of economic growth, there’s generally an uptick in consumer confidence, which leads to increased spending and, consequently, can fuel inflation. Conversely, during economic downturns, inflation rates often decrease as consumer spending decreases.
Given this relationship, investors must gauge a country’s economic climate before making investment decisions. For instance, during the economic boom of the late 1990s in the United States, fueled by the dot-com bubble, there was a considerable rise in inflation. Investors who had diversified their portfolios with inflation-protected assets such as TIPS or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) would have seen their investments hold value even as the dollar’s purchasing power diminished.
Industry and Sector Performance
The performance of specific industries or sectors can also influence inflation rates, making it a critical factor to consider when selecting investments that guard against inflation. For instance, certain industries like energy and food are more sensitive to price fluctuations driven by supply and demand, which can impact the overall inflation rate.
Investing in industries with higher price sensitivity, such as commodities, can help mitigate the effects of inflation on an investment portfolio. Additionally, certain sectors, like real estate and infrastructure, have historically strongly correlated with inflation rates. Therefore, investing in these sectors can protect rising prices.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
Supply and demand dynamics are crucial in determining the overall inflation rate. Inflation is caused by increased money supply compared to the available goods and services in an economy, leading to higher prices. Therefore, understanding how supply and demand impact different investments is essential for building an inflation-proof portfolio.
For instance, real estate can be considered a relatively safe investment against inflation due to its limited supply. As the population grows, demand for housing increases, driving up prices and making real estate a potential hedge against inflation. Similarly, investments in commodities like gold or oil can also offer protection as global supply and demand dynamics influence their value.
In contrast, investments with an inflation-adjusted principal, such as stocks, can be more susceptible to price fluctuations driven by excessive supply, making them less suitable for inflation-proof portfolios. Understanding the supply and demand dynamics of different assets can help investors choose investments best suited to protect against inflation.
Benefits of Diversification in Inflation-Proof Investments

As discussed, there are various factors that influence inflation rates and affect the performance of different investments. Therefore, diversifying an investment portfolio with a mix of assets can provide significant benefits in protecting against inflation. Here are some key advantages of diversification:
- Reduces overall risk: By spreading out investments across different asset classes, investors can minimize their exposure to risk. This is because different assets react differently to changing economic conditions and market fluctuations. Therefore, if one investment underperforms due to inflation or other factors, the impact on the entire portfolio will be minimal.
- Mitigates volatility: Inflation can lead to market volatility, causing prices of assets to fluctuate rapidly. By diversifying investments, investors can mitigate this volatility and potentially see more consistent returns.
- Provides a hedge against inflation: Different investments have varying sensitivity levels to inflation. By diversifying with inflation-hedging assets like commodities or real estate, investors can protect the purchasing power of their portfolio even in times of high inflation.
- Offers potential for higher returns: Diversification allows investors to tap into a wider range of investment opportunities, potentially leading to higher overall returns. By allocating investments across different industries and sectors, investors can capitalize on growth areas while mitigating the effects of downturns in other sectors.
Conclusion
Inflation can significantly impact an investment portfolio, eroding the purchasing power of money and diminishing returns. However, by understanding the various factors that influence inflation rates and selecting a diversified mix of inflation-proof investments, investors can effectively hedge against inflation. This includes commodities, real estate, and certain industries and sectors. Additionally, understanding the dynamics of supply and demand and the economic conditions can help investors make more informed decisions. Effective diversification and strategic asset allocation are key to protecting an investment portfolio against inflation.